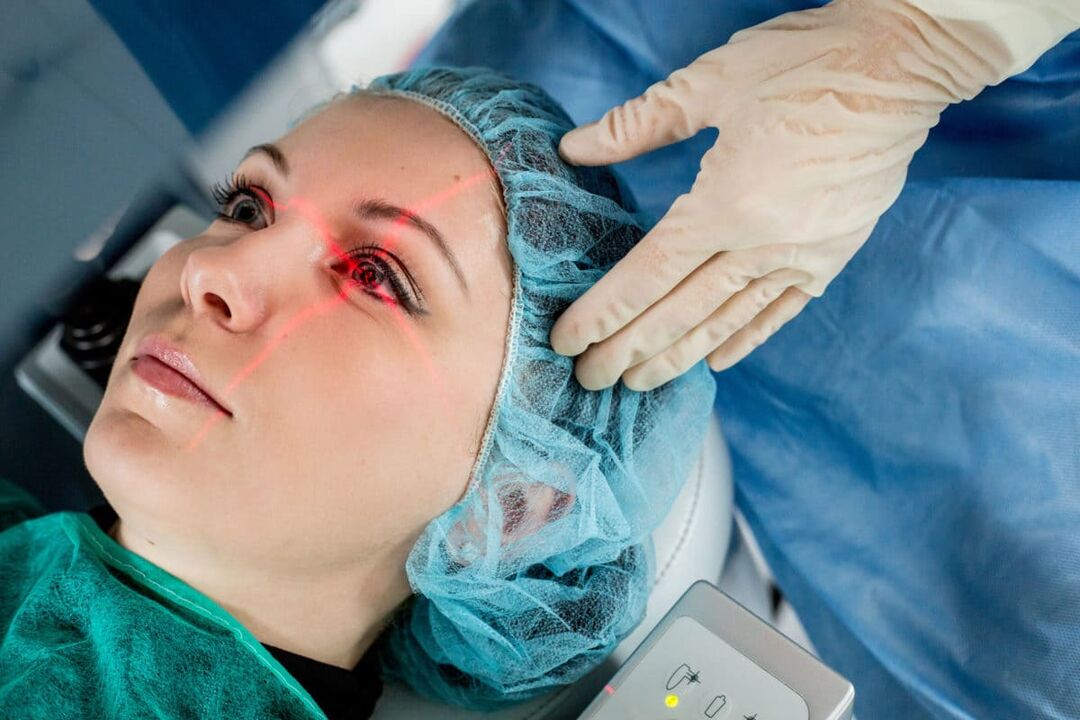
Laser vision correction has become one of the most popular and effective methods for eliminating various types of visual defects. The absence of frames and contact lenses, the ability to see clearly without the help of aids - all this makes laser correction the most attractive option for many people with nearsightedness, farsightedness, astigmatism and other vision problems.
Laser eye surgery uses advanced technology to precisely and safely reshape the cornea. This is necessary to correct the refractive power and, therefore, improve the quality of vision. The surgery is performed using a high-precision laser that modifies the eye tissue with minimal risk and complications for the patient.
However, given the specificity and cost of such an operation, it is certainly useful for many people suffering from ophthalmological diseases to know about the benefits and possible risks associated with the procedure. We will also see how to choose the right specialist and prepare for surgery to achieve the best results.
What is laser vision correction and in what cases is it performed?
Laser vision correction, also known as laser refractive surgery, is a modern procedure that uses laser equipment to correct vision problems and eliminate dependence on glasses or contact lenses. The main goal of laser vision correction is to reshape the cornea, the transparent front of the eye, to allow light to focus precisely on the retina.
This is achieved by removing a microscopic layer of tissue from the cornea using a laser beam, which changes its curvature and therefore improves the focusing of light. This procedure allows patients to eliminate the need to wear glasses or contact lenses, improving the quality of their vision.
Instructions for operation:
- Myopia (myopia). This is a condition where a person has trouble focusing on distant objects due to excessive focusing of light in front of the retina. Laser vision correction can reshape the cornea so light is focused on the retina, improving distance vision.
- Farsightedness (hypermetropia). A condition where a person has difficulty seeing close objects clearly, usually caused by a refractive error. The operation allows you to correct the disease, and only in 1 procedure.
- Astigmatism. Vision disorders where the cornea or lens of the eye is asymmetrical or irregular in shape. This results in distorted focusing of light on the retina of the eye, which in turn results in blurred and distorted images at both near and far distances.
Laser vision correction is considered a safe and effective procedure to correct almost all vision defects. However, before deciding to undergo the procedure, it is important to undergo a detailed eye examination and consult with an experienced ophthalmologist to determine the appropriate method, evaluate possible risks, as well as benefits for each specific case.
When is laser vision correction recommended?
Laser vision correction, also known as laser refractive surgery, may be recommended in the following primary cases:
- Intolerance to contact optics. If the patient has difficulty wearing contact lenses or causes various problems, including discomfort, allergic reactions or damage to the cornea, laser correction may be recommended as an alternative to correct vision.
- Profession or type of activity. Many professions require excellent vision where glasses or contact lenses cannot be worn—aircraft pilots, military personnel, athletes, or firefighters. Laser correction may be recommended to improve vision and ensure independence from corrective aids.
- Myopia (from -1 to -15 diopters), farsightedness (from +3 diopters), and astigmatism (up to +5 diopters). Corrective surgery can improve near vision and eliminate the need to wear glasses or contact lenses for close work.
Laser correction can also be effective in correcting astigmatism, which can be severe and reach values of up to +5 diopters. Patients with astigmatism may experience blurred and distorted vision, and laser correction can help correct this problem.
The type of vision correction surgery performed
Specialists prescribe various procedures and methods designed to improve the vision of people with certain problems or defects in the visual system. However, if we talk about operations, they can be divided into 2 large categories:
- LASIK (Assisted in situ Keratomileusis). One of the most common laser vision correction procedures, the surgeon creates a thin flap-shaped skin on the cornea, then lifts it to reveal the depth of the correction, and uses a laser to remove a thin layer of corneal tissue. The valve is then reattached in place, ensuring quick healing and minimal pain.
- PRK (photorefractive keratectomy). An alternative surgical option to restore visual clarity where the superficial layer of the cornea is completely removed and a laser is applied directly to the exposed surface. After the procedure, the cornea heals on its own, although it takes some time to restore vision.
However, before making the final decision to undergo vision correction surgery, it is necessary to consult with an experienced ophthalmologist. This allows you to correctly assess the situation and choose the most suitable method, taking into account the characteristics of the visual system and the wishes of a particular patient.
Contraindications for laser vision correction
In general, laser vision correction is considered a safe and effective procedure for many people with certain types of refractive disease. However, it is important to remember that there are also some contraindications that can make this procedure unsafe for some patients. The main contraindications for laser vision correction include:
- childhoodLaser vision correction is not recommended for children and teenagers because their eyes are still developing.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding. During this period, women may experience changes in visual acuity, so it is recommended to postpone the procedure until the end of breastfeeding.
- Changes in refraction. Laser correction is not recommended for patients with active changes in clarity due to conditions such as diabetic retinopathy or glaucoma.
- Physical damage to the cornea. If the patient has scars, ulcers, or other corneal irregularities, laser correction may not be an appropriate or safe procedure.
- Dry eyes. Patients who frequently experience a burning sensation in their eyes may experience worsening symptoms after laser vision correction treatment.
- Corneal disease. Laser vision correction is not recommended for patients with conditions such as keratoconus or corneal dystrophy.
- Problems with the fundus of the eye. Patients with certain fundus diseases, including macular degeneration or diabetic retinopathy, may have restrictions on surgery.
- Autoimmune disease. People with autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, or Sjogren's syndrome) may have an increased risk of complications after laser surgery.
- Eye infection or inflammation. If there is an active eye infection, inflammatory process or conjunctivitis, it is recommended to postpone laser correction until complete recovery.
- Taking certain medications. Some drugs that affect the immune system can also affect the healing process after laser correction, so their use may be contraindicated.
The list of contraindications may vary depending on the individual characteristics of the patient and the doctor's recommendation. Before undergoing laser vision correction, it is necessary to undergo a thorough examination and consultation with a specialist to assess the patient for any contraindications and decide on the possibility of the procedure.
How laser vision correction works: surgical stages
Often, eye surgeons perform LASIK, which can help improve the vision of people with nearsightedness (myopia), nearsightedness (hyperopia), or astigmatism. Here are the main steps of LASIK surgery:
- Preliminary examination. Before surgery, the patient must undergo an initial eye examination, including measuring vision, checking the shape of the cornea, its thickness and the general condition of the eye.
- Anesthesia. Before the surgery begins, the patient's eyes are numbed with anesthetic drops.
- Creation of the corneal valve. The surgeon creates a small valve in the cornea using a mechanical device or a laser. To create the valve, microkeratome or femtosecond laser methods can be used.
- Vision correction. After creating the corneal valve, the doctor uses an excimer laser to remove a thin layer of corneal tissue. This changes its shape to correct vision errors. In the case of myopia, the middle part of the cornea is made flat, and for hyperopia, it is made steeper. To correct astigmatism, the shape of the cornea is changed accordingly.
- Close the valve. Once the vision correction is complete, the surgeon carefully closes the corneal valve that was created. It usually repairs itself without needing stitches.
After the operation is completed, the patient is advised to rest and avoid straining the eyes, because the vision may become blurred or blurry for a few hours, but in most cases everything returns quickly.
Benefits of laser vision correction
Recently, more and more people have decided to restore their vision using laser correction. Here are the advantages:
- High efficiency. Laser vision correction is one of the most successful vision correction methods today, as this procedure allows people to significantly improve their vision.
- Quick recovery. After laser correction, most patients note a very quick recovery of vision. Within a few days after the procedure, they can return to daily activities and even resume driving.
- Eliminates the discomfort of contact lenses and glasses. This procedure allows people to eliminate the need to wear glasses, which is ideal for people who play sports or lead an active lifestyle.
- The duration of the results obtained. In most cases, the results of laser vision correction are stable and long-lasting. After the procedure, many patients receive stable vision, and some do not need additional correction.
- Personal approach in a reliable clinic. Modern technology of laser vision correction allows the procedure with a high degree of individuality. Doctors use state-of-the-art equipment to create accurate corneal maps and analyze other factors tailored for each patient. This allows for maximum accuracy and results that best suit each individual's needs.
- Comfort and convenience. After laser vision correction, patients no longer have to worry about having glasses or contact lenses with them at all times. This brings significant convenience and comfort to everyday life.
- Various fixes. Laser vision correction can be used to correct various types of refractive errors, such as nearsightedness (myopia), farsightedness (hyperopia) and astigmatism. This means that most people with these vision problems can be candidates for this procedure.
- Speed. Laser vision correction itself usually only takes a few minutes per eye. This is a very fast process that allows patients to get the results they want quickly and return to their normal activities.
- Low risk of complications. Modern laser vision correction procedures have a low risk of complications. Thanks to advances in technology and the experience of doctors, complications are unlikely to occur and most patients achieve a safe and successful outcome.
Laser vision correction can significantly improve the patient's quality of life. The ability to see clearly without the aid of glasses or contacts provides greater freedom and independence in everyday life, boosts confidence and encourages an active lifestyle. Overall, laser vision correction provides many unique benefits, including high efficiency, quick recovery, and no contact lens inconvenience.
Undoubtedly, laser vision correction has become a real success in the field of ophthalmology, helping millions of people around the world get rid of dependence on glasses and contacts. However, before deciding on such a serious procedure, it is important to familiarize yourself with its features, risks and potential benefits. Only then can you make informed decisions and increase your chances of achieving a clear and comfortable vision for the next few years.